The Ultimate Guide to Stakeholder Management
Effective stakeholder management is integral to successful projects. That’s because stakeholders can have a significant impact on business outcomes. Organizations that maintain positive relationships with stakeholders can better identify and address stakeholder concerns, thus building trust and improving their reputation. Creating a detailed stakeholder management plan and putting it into practice will help you align with the varied priorities of stakeholders, enhancing your likelihood of success.
In this guide, we will outline everything you need to know about effective stakeholder management, from understanding what stakeholder management is, to creating a successful stakeholder management plan and best practices. We’ll also outline why organizations trust our software to manage stakeholders efficiently, ensuring project success and securing a social license.
What is stakeholder management?
When talking about stakeholder management, we refer to identifying, analyzing, and engaging with individuals or groups with an interest or concern in a project, organization, or decision. The primary objective of stakeholder management is to consider and address the needs of all stakeholders fairly and transparently. This approach helps to build trust and minimize any potential negative impacts that may arise.
Effective stakeholder management is essential for your organization to secure necessary project permits, handle complaints and grievances, gain stakeholder support, and stay updated with legislative developments that could impact your organization’s financial performance.
the stakeholder management process
Why is stakeholder management critical?
Improved stakeholder relationships
Reduced risk
Organizations that effectively engage stakeholders can better anticipate potential issues and address them proactively before they escalate into significant grievances or work stoppages, which can jeopardize project success.
Increased innovation
Better reputation
Better decision-making
Regulatory compliance
Social responsibility

Real-world stakeholder management
How to identify your stakeholders in a stakeholder management process
The first step to managing stakeholders effectively involves identifying all the individuals and groups involved. This process includes internal and external stakeholders, such as employees, customers, suppliers, regulators, shareholders, community members, government officials, and industry, environmental and indigenous groups.
It is essential to create a comprehensive list of these stakeholders who may be interested in, affected by or hold influence over your project or activities. When identifying stakeholders, it is essential to take a broad approach and recognize all entities that can influence or be influenced by the organization’s decisions and actions.
| Identifying internal stakeholders | Identifying external stakeholders |
|---|---|
|
|
| Identifying internal stakeholders |
|---|
|
| Identifying external stakeholders |
|---|
|
Once you have identified your stakeholders, it is time to consider stakeholder mapping.
Stakeholder mapping enables you to visualize your relationships with stakeholders. By helping you identify those with power or influence over your project, you can better engage with them.
A stakeholder map captures a specific moment in time. It is a snapshot. This makes it essential to periodically remap your stakeholders so you can see how their positions change over the life of your project.
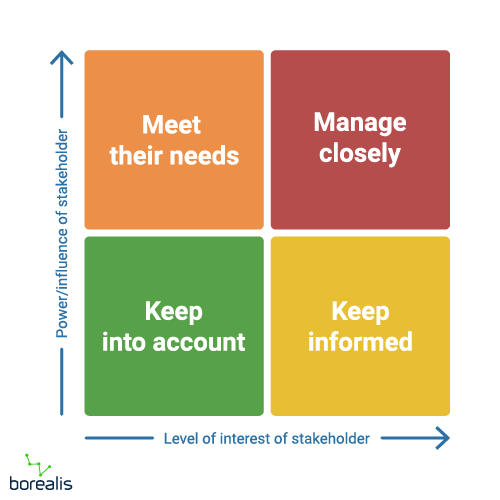
A stakeholder map is often depicted as a graph with two axes divided into four quadrants. The x-axis represents a stakeholder’s level of power or influence, while the y-axis indicates their level of interest in your project. Each quadrant on the map requires a different engagement strategy. A stakeholder’s position will determine how you engage with them, including the intensity and frequency of engagement.
By mapping out the level of power and influence and the level of interest of each stakeholder, you can determine the most appropriate engagement strategy, including the intensity and frequency of engagement. However, stakeholder mapping is not just about illustrating relationships; it also helps you identify key stakeholders and prioritize them accordingly.
Without engaging in stakeholder mapping, you may allocate valuable resources in the wrong places. At best, this can increase project costs and create unnecessary delays. In more extreme cases, it can lead to work stoppages and even damage your corporate image.

Conducting a stakeholder analysis
Stakeholder analysis is a crucial process used to identify and assess the significance, influence, interests, or impact of various stakeholders in relation to a project or business decision. The primary objective of stakeholder analysis is to ensure that the needs and opinions of stakeholders are considered, thereby enabling better decision-making and the effective management of potential conflicts or issues.
The four steps of stakeholder analysis
Step 1:
Identify your stakeholders
Step 2: Understand your stakeholders
Step 3:
Group your stakeholders
Step 4: Evaluate your key stakeholders
Perform stakeholder analysis early in the project and repeat regularly to track stakeholder evolution and changing needs, expectations, and relationships. This ongoing exercise will provide insights to develop engagement strategies and show how stakeholders are evolving proactively. Each analysis is a snapshot of a certain point in the project timeline and will reveal key stakeholders, shifting needs and expectations, and relationship changes.
Ready to dig deeper into stakeholder analysis? This blog has everything you want to know.
How to create an effective stakeholder management plan
Effective communication is critical for successful on-site and remote project management. Though planning is daunting, it can determine your project’s success and failure.
A stakeholder engagement plan must consider every individual, organization, business, family, governmental institution, indigenous group, piece of land, tree, crop, or animal affected by the project. That may sound like many stakeholders, but some projects involve that level of detail.
What is a stakeholder management plan?
A plan for engaging stakeholders is primarily focused on strategic communication. A Stakeholder Management Plan is a step-by-step guide that lays out how your organization will communicate with stakeholders to increase the chances of achieving positive outcomes for your project.
It’s a written document that identifies the main stakeholders and explains how you interact and communicate with them. This document enables your project manager to create a strategy for managing expectations and delivering the correct information to the right people at the right time.
A stakeholder management plan is closely connected to stakeholder analysis. These elements are designed to help you determine the best ways to communicate and convey messages effectively. This can assist in reducing negative perceptions, amplifying positive effects, and resolving conflicts before they become more serious.
Preparing a Stakeholder Engagement Plan (SEP)
Our experience has proven that a good stakeholder engagement plan consists of 12 sections. A detailed analysis can be found in this article.
- 1. Areas of influence
This first section provides a geospatial understanding of the areas impacted by the project. It also determines the level of engagement according to each zone (based on a scale from negligible to significant). - 2. Regulations and requirements
Most development projects must respect many regulations and requirements. Organizations must ensure compliance and conformity throughout the project. - 3. Methodology
Choosing a practical methodology is vital as it forms the foundation of your plan, outlining stakeholder identification and categorization criteria. - 4. Project stakeholders
In this section of your Stakeholder Engagement Plan, you’ll develop an all-inclusive directory of each group and sub-group you previously identified in your methodology. This list encompasses various details, including traditional and customary authorities, villages, and much more. - 5. Stakeholder engagement activities
The “activities section” of your stakeholder engagement plan is a crucial component that outlines your communication strategies for each group you identified during the stakeholder analysis process. This section ensures you comprehensively understand the unique needs and preferences, allowing you to tailor your communication strategies accordingly. - 6. Stakeholder engagement plan template
Now that we’ve identified your stakeholders and how you’ll reach them, this section of your stakeholder engagement plan will cover how to implement your strategy. We can help. Download our Stakeholder Engagement Plan Template.
- 7. Timetable
This section will provide an overview of your communication strategy for each project phase over time. You don’t need to go into too much detail. We recommend monthly intervals. - 8. Resources and responsibilities
When coordinating activities, clearly outline each team member’s responsibilities and hierarchy for grievance escalation. Create job descriptions with names and an organizational chart for a visual overview of responsibilities. Indicate external contractors’ roles and positions. - 9. Grievance management
Stakeholders should be able to request and receive a clear definition of what constitutes a grievance and how it is managed, including an estimated resolution time. - 10. Monitoring and reporting
Using a stakeholder relationship management system (SRM) is more efficient and secure than patchwork tools like email, spreadsheets, and shared documents. With an SRM, all data is centralized, saving time when looking for specific information from past interactions. - 11. Budget
You’ll also need to monitor the financial aspects of your stakeholder engagement activities. Make sure to enter as much detail into your budget as you can. Also, remember to review your budget often. - 12. Appendix
In the Appendix, you’ll incorporate documents like your PAP list, templates for grievance forms, and attendance sheets for public consultations. Including links to other relevant documents related to your stakeholder engagement plan could be beneficial.

Building long-term stakeholder relationships in the rail industry
The CN rail team didn’t have any formal tool or system for keeping track of all their stakeholder communication. Here’s how our software was a game changer.
Stakeholder management best practices
Cultivating solid relationships with stakeholders is crucial for successful engagement. However, it’s important to note that fostering a ‘good relationship’ doesn’t guarantee constant satisfaction among all stakeholders.
Ultimately, positive stakeholder relationships are grounded in trust. Effective communication plays a central role; thus, establishing transparent and accessible communication avenues where individuals feel valued and heard is essential. Let’s explore strategies to enhance stakeholder relationships.
Conduct a thorough stakeholder analysis.
Be as accessible as possible.
Communicate clearly and honestly.
To build good relationships with stakeholders, treat them how you want to be treated. Always be honest and direct in your communication, and don’t make commitments you’re unsure of. It’s essential to be realistic and manage expectations by being clear about which decisions have been made and what’s still uncertain. Share information as it becomes available and continue to communicate throughout the project.
Show stakeholders that you’re listening.

SRM vs. CRM software: What’s the difference?
We’ve detailed the stakeholder management plan and explored the best practices. It’s time to talk about managing all the data and information produced during your stakeholder engagements.
There are many ways to do this. Common strategies often entail utilizing a mix of Excel spreadsheets, emails, shared documents, and more. However, this amalgamation of tools often undermines data security and traceability, making it inefficient for monitoring and reporting.
One of our clients, Guinea Alumina Corporation (GAC), faced a significant challenge; overseeing the compensation process for the eight communities requiring resettlement. The predominantly manual process that relied on spreadsheets was inefficient and created timing bottlenecks. Learn how our SRM helped them use their time and money more effectively.
That case study exemplifies why adept stakeholder engagement teams leverage a digital solution that unifies data in a single space. There are two options: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software and Stakeholder Relationship Management (SRM) software.
In reality, SRM and CRM software are not interchangeable; they serve very different objectives. But what’s the difference between SRM and CRM systems… and which one is right for you
What is SRM software?
Benefits of Stakeholder Relationship Management Software
SRM Software is most useful for organizations concerned with the following:
- Community engagement
- Public affairs and government relations
- Asset and land management
- Environmental and social performance
What is CRM software?
The differences between SRM and CRM software
Goal
The risks of using spreadsheets to manage stakeholders
Are you managing vast amounts of stakeholder data using spreadsheets? You’re taking a considerable risk.
Sure, spreadsheets are still the most widely used tool for managing stakeholder data. But, they are certainly not the recommended best practice.
What makes spreadsheets so risky? Put simply: time and money. Spreadsheets are time-consuming and prone to errors. Nor do they follow data security best practices. And they’re certainly not designed to track stakeholder engagement.
Stakeholder engagement software, like Borealis, is a more efficient way to manage stakeholder data. It is especially pivotal if you manage many stakeholders, projects, and team members.
If you worry about transferring all those spreadsheets into your stakeholder engagement software, you’re in luck. Importing data from spreadsheets to these specialized systems is quite straightforward. In fact, we even handle data migration for you.
Learn more about the risks of relying on spreadsheets and the real difference that stakeholder engagement software can make.
How to choose the right stakeholder management software
Using an SRM to manage stakeholder engagement has many advantages. Firstly, it saves you a lot of time since all data is centralized in one place. You can easily retrieve specific information from interactions that took place years ago.
Some systems even provide advanced analytical tools to help you compile quick reports and extract valuable insights from your data. You can access detailed information about areas, subjects, and resolution times with just a few clicks. Additionally, you can effortlessly generate monthly reports of your team’s engagements with trends.
Borealis stakeholder management software offers all this and more. It goes beyond planning by providing software that breaks down your engagement plan into actionable activities and assigns tasks to your team. The Stakeholder Engagement Plan feature gives you a real-time view of your progress as the project unfolds, allowing you to adjust course quickly as needed. Proper planning helps minimize oversights, eliminate duplicate efforts, and simplify the reporting proce
Why choose Borealis as your SRM?
The user-friendly interface is designed for simplicity, accommodating even those less familiar with technology. Borealis streamlines data entry and searches, fostering user acceptance and enabling teams to concentrate on cultivating reliable stakeholder relationships rather than data management.


